Machine Information
Processor Features
There are multiple levels of feature that a CPU must implement according to the processor specification. These are called micro-architecture levels. For x86-64, these are: x86-64-v2, x86-64-v3 and x86-64-v4 .
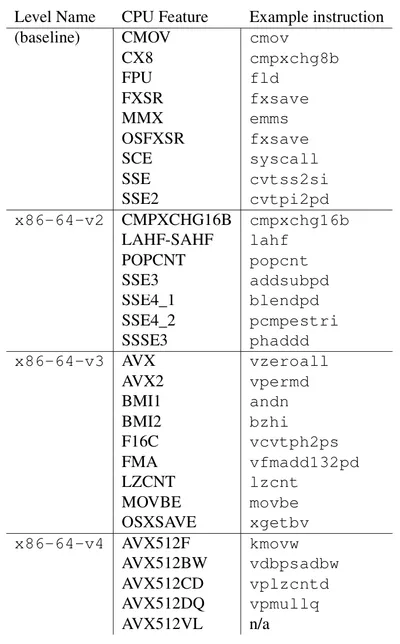
Fig 1.1 - CPU Micro-architecture levels
- Levels
x86-64-v3andx86-64-v4are only available if the features are fully enabled. - The names are expected to be used as directory names by linkers and compilers.
- To build with a given level, the programmer can build a shared object using
-march=x86-64-v3(or other suitable) GCC flag. - The resulting shared object is then installed in
/usr/lib64/glibc-hwcaps/x86-64-v3or/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/glibc-hwcaps/x86-64-v3.
Data Types — Size and Alignments
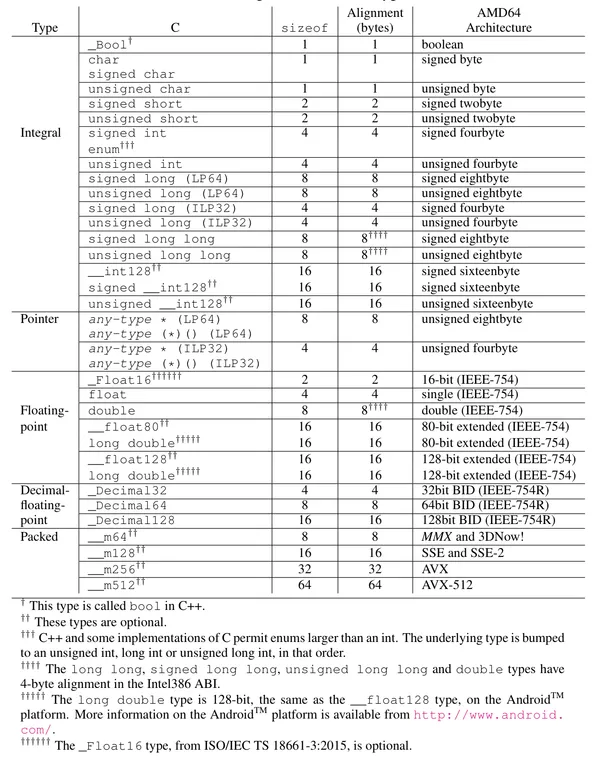
For types of N-bit integers
- If : they have the same size and alignment as the smallest scalar type (
char,short, etc.) that can contain them. - If : treated as struct of 64-bit integer chunks.The size is the where is the number of chunks that can contain the type, but the alignment is 64-bits.
For Bitfields:
- They are allocated from right to left.
- Must be contained in a type that can store them.
- Can be shared using unions and with other struct members.